8 Lessons from Our #2 GitHub Trending LLM Agent
Our open-source project hit #2 on GitHub Trending. Believe it or not, we only spend a weekend on it. Here are 8 lessons we learned.
Project: MLE-Agent
Lesson 1: Start with Real Needs
As a Machine Learning Engineer (MLE), I deal with data processing, reading papers, debugging code, and others every day, which are exhausting.
One day I thought, why not create an agent to automate some of these repetitive tasks?
I checked with some MLE friends, and they all thought it was a good idea. Then I decided to give it a go with my friends right now.
Lesson 2: Leverage Trends
Lately, projects like SWE-Agent and Devin have been all the rage in Silicon Valley. People realized that agents can boost Software Engineers (SWEs)’ productivity.
But as MLEs, we know our tech stack is different from SWE’s.
Then we thought how about leveraging this trend to promote MLE-Agent.
The project may fail later but as people’s attention is here now, we can get many valuable feedbacks.
Lesson 3: Get MVP Done
MLE roles vary widely, facing different business scenarios, data types, and tech stacks. If you aim for universality from the start, you might run into endless problems.
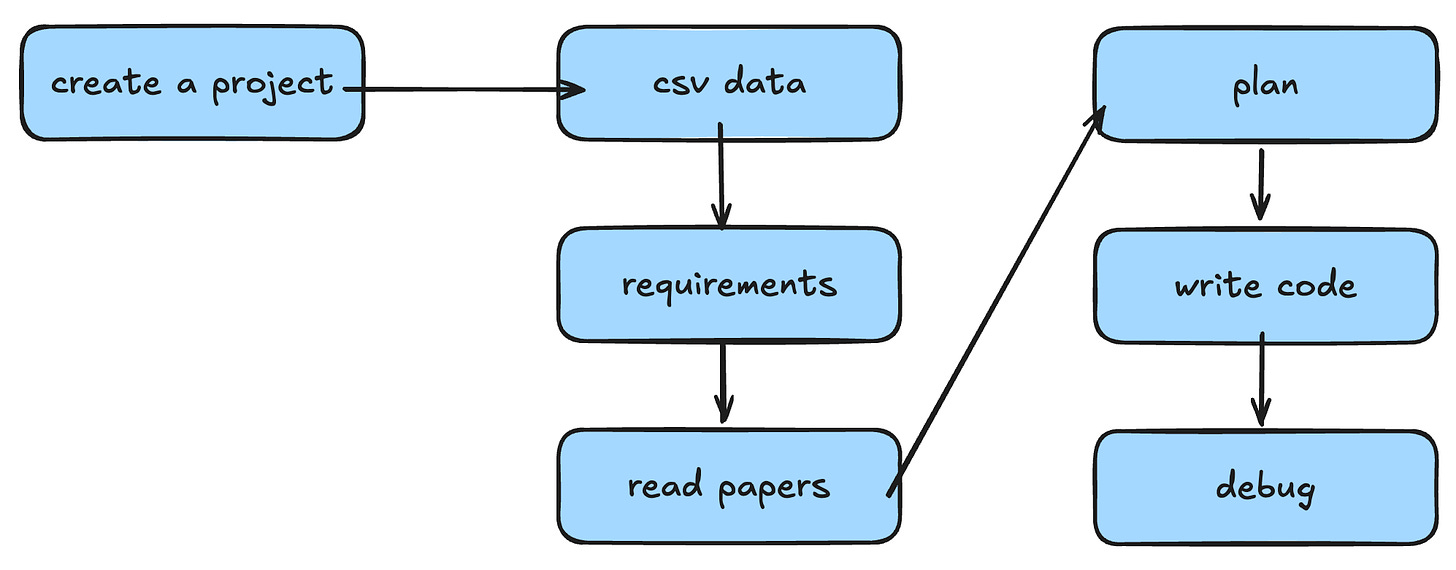
Therefore, we began with automating the simplest workflow: create a project → read CSV data → understand user requirement → read papers → come up with a good experiment design → write code → debug and test code.
After we flesh out the details of this workflow, how to get MVP (minimal-viable-version) done becomes clear to us.
Lesson 4: No Frameworks
We developed MLE-Agent using purely OpenAI API, without relying on any frameworks like LangChain.
As our MVP is super small, no frameworks saved us time on learning and testing, making development faster.
Lesson 5: Define Project Goals Clearly
Before we start, we envision the final form of MLE-agent first. We write a detailed project README by mimicking top-tier projects, even if we have nothing.
But we do not want to lie to people, so we clearly outline what’s done and what’s not in the roadmap section along with our development. As a result, people have a clear view of the project’s status.
Lesson 6: Keep Up with Updates
After we finished the MVP, we decided to fix one small bug per day and release a small feature per week.
By doing so, we kept the project updated on GitHub, which helped it get noticed by recommendation algorithms.
Lesson 7: Be Patient with Cold Starts
Actually, there are very few stars at the beginning.
We believe that as long as we focus on delivering value, the recommendation algorithms will eventually take notice.
Lesson 8: Help People, Enjoy the Process
We know that our goal is to make our lives easier first and don’t worry too much about its popularity.
We also know that this will definitely help people after many iterations.
We really have fun with it.
We have nothing to lose.
Thanks for reading this.
I’m excited to share more about our agent development journey and hope you find it useful.



super useful content!